Every email marketer dreads receiving a bounce alert after investing long hours crafting the perfect email campaign. Even though emails bounce occasionally, they show an underlying issue from the sender’s or recipient’s end.
Also, frequent bounces negatively impact your email sender score and deliverability rate, which is not good for your email campaigns in the long run. So, keeping the email bounce rate within a healthy limit is best.
In this blog post, we cover all you need to know about bounce back emails, the types, causes, tips to reduce your bounce rate, how it is calculated, and an FAQ section that addresses the additional questions you may have.
Table of Contents
What is a Bounce Back Email?
A bounce back email, also known as a failed delivery message, is an automated response informing you that your email has not been delivered to the intended recipient.
Think of it as a game of basketball where not every shot you throw bounces into the hoop. Some miss and bounce off. In the same way, not all emails sent makes it to the recipient’s inbox: some bounce back.
Your email service provider sends you a Non-Delivery Report (NDR) showing that your email wasn’t delivered, just like when you send a physical letter that gets returned to you because the address is incorrect or the recipient is no longer there.
Email bounce occurs for various reasons, such as the recipient’s inbox being full, incorrect email address, server issues, or the recipient’s email provider identifying the email as spam.
An email bounce notification typically contains details about the original message, like the date and time it was sent and the reason for the delivery failure, thus allowing you to rectify the issue.
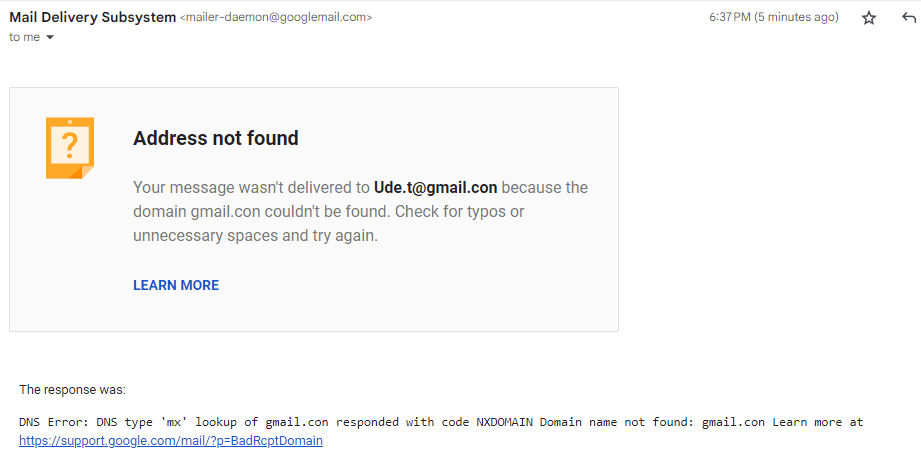
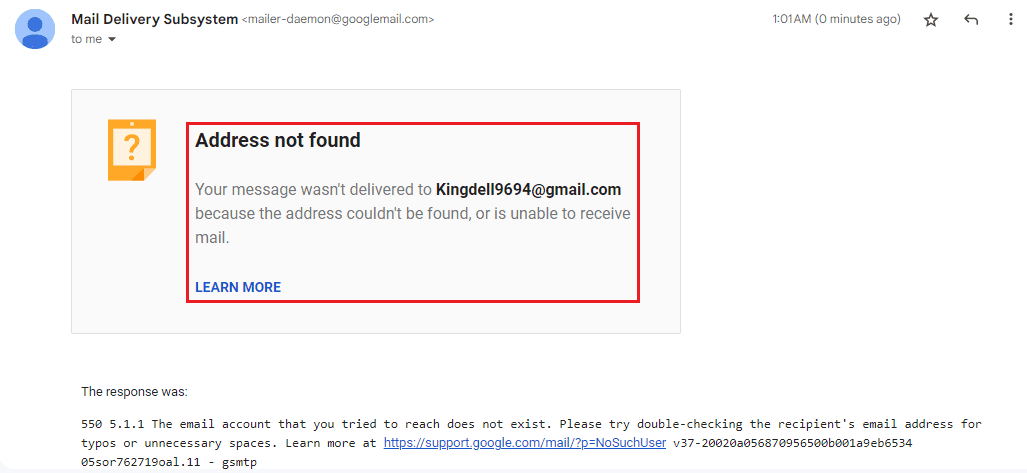
The non-delivery report in the image above shows that the email bounced because of an incorrect domain address and suggests how to fix it.
Types of Email Bounce
Depending on the cause, bounce back emails can be categorized into Hard, Soft, Transient, or General Bounce. Let us take a close look at each of them.
Hard bounce
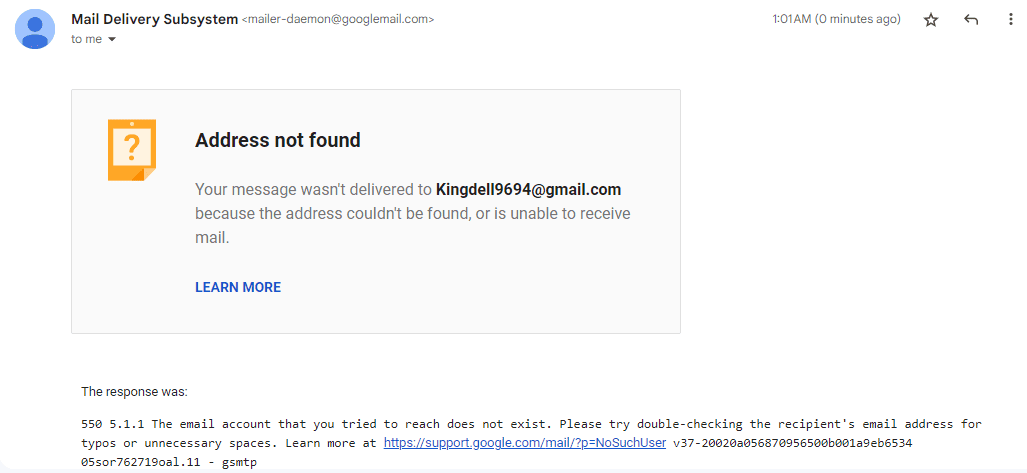
- Invalid email address: This is the most common cause of a hard bounce. It occurs when you send an email to an address that doesn’t exist or is misspelled. This is why it is essential to double-check the accuracy of email addresses before adding them to your mailing list.
- Non-existent domain: When the domain in the email address doesn’t exist, the email cannot be delivered, leading to a hard bounce. For example, an email sent to John@gmail.con instead of John@gmail.com will be bounced due to an error in the domain name.
- Unknown recipient: If the recipient’s email server identifies the recipient as unknown, it will reject the email, resulting in a hard bounce. This can happen if the recipient has changed their email address or if there is a mistake in the email address.
How to deal with a hard bounce
If unchecked, hard bounces can reduce your email send score and harm your email deliverability. Here are a few things you can do to prevent a hard bounce.
- Remove invalid email addresses: It’s crucial to promptly remove from your mailing list all email addresses that have bounced. Continuing to send emails to invalid addresses can harm your sender’s reputation and email deliverability.
- Update contact records: Ensure you update your contact records to reflect the status of hard-bounced email addresses. This will prevent you from using these addresses in future email campaigns.
- Maintain a clean mailing list: Update your mailing list regularly to remove invalid or inactive email addresses. This practice will help you maintain an active email list and improve your email campaign success.
Read also: Bounce Rates and Email Deliverability – A Simple Guide
Soft bounce
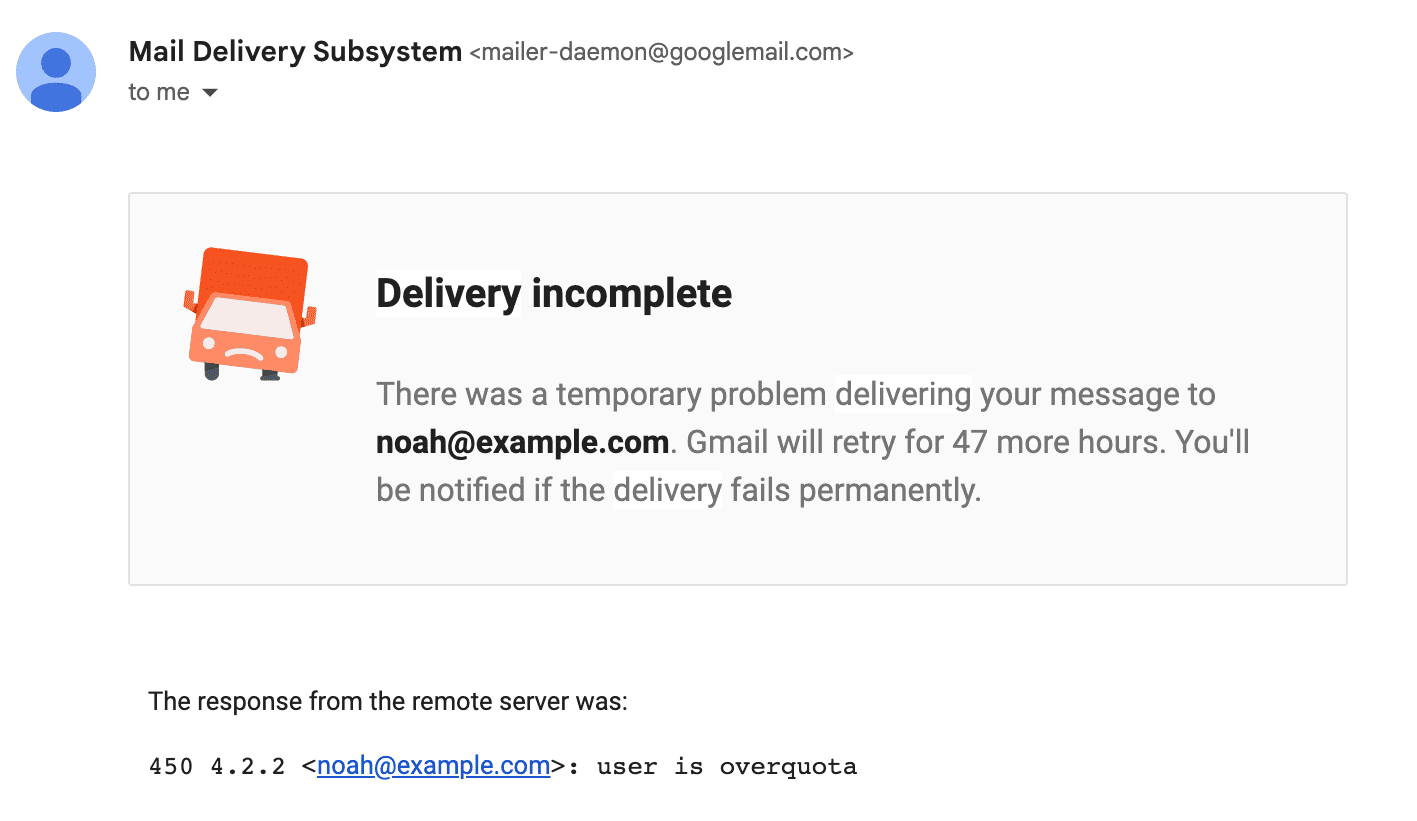
- A full mailbox: When a recipient’s mailbox is full, it cannot accept any new messages. This could indicate an abandoned mailbox or a need for the recipient to clear their inbox.
- Temporary network issues: A soft bounce may sometimes occur due to transient network problems on the recipient’s end. These issues could include server outages, connectivity problems, or other technical glitches. In such cases, the email delivery failure is not permanent, and you may be able to resend the email in the future successfully.
- Message size limit exceeded: If your email contains large attachments, it may exceed the recipient’s mailbox size limit. This can result in a soft bounce. To avoid this, consider compressing or resizing attachments before sending them.
How to deal with a soft bounce
When you encounter a soft bounce, there are steps you can take to address the issue and improve your email delivery rate.
- Retry sending: In case of a temporary issue, you can attempt to resend the email later. Some email service providers automatically retry sending for a certain period before marking an email address as bounced.
- Check for spam: Ensure your email content isn’t triggering spam filters. This includes checking for spammy words, excessive use of caps and exclamation marks, and large attachments.
- Reduce the size of your email: Large emails often lead to soft bounces as some email servers have limitations on the size of emails they can receive. So, reducing the size of your email could resolve a soft bounce alert.
Read also: Learn To Manage Email Bounce Codes In 10 Minutes
Transient Bounce
A transient email bounce is a temporary delivery failure of an email due to issues with the recipient’s server, such as overloading or undergoing maintenance.
Unlike hard bounces, which are permanent failures because of invalid email addresses or domain errors, transient bounces are often resolved over time. The sender’s email server will usually attempt to resend the email regularly until it is successfully delivered or the delivery fails permanently.
General or unspecified bounce
Due to its ‘unspecified’ nature, this type of bounce is harder to rectify. A general or unspecified bounce is a delivery error message triggered due to unspecified or general reasons. This could include a range of issues, such as temporary server problems, unfiltered messages, or other factors that prevent the successful delivery of the email.
Read also: Email Deliverability: 7 Tips To Get More Clicks, Sells & Signups
Email Bounce Rate 101
The email bounce rate is the percentage of emails not delivered to the recipient’s inboxes.
A low bounce rate is like the slam dunk in email marketing. It means more of your emails are reaching their intended targets, which could lead to higher engagement and, ultimately, more conversions for your business.
According to Statista, the average daily email bounce rate in the United States is 0.4% and rises to 1.3% once a month.
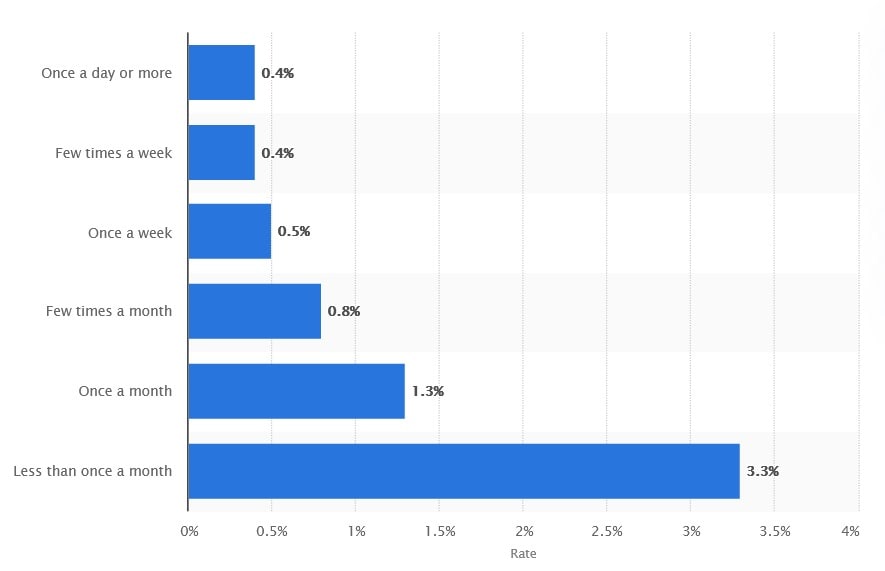
Furthermore, a HubSpot report showed that the average email bounce rate across industries is 0.63%.
Generally, a healthy email bounce rate is between 1% and 2%. An email bounce rate above 2% indicates a significant problem with your email marketing campaigns.
Now that we’ve known what an email bounce rate is, let’s head over to how you can calculate it.
How to calculate your email bounce rate
To calculate your email bounce rate, you must determine the percentage of bounced emails out of the total number of emails sent. Here’s the formula:
Bounce Rate = (Number of Bounced Emails / Total Number of Sent Emails) × 100
Suppose you sent 1,000 emails as part of your campaign, and 30 bounced back. Your bounce rate will be 3%.
Bounce Rate = (30 / 1,000) × 100 = 3%
In this example, the bounce rate would be 3%.
Consider the following recommendations to enhance your understanding of email bounce rates.
Utilize email marketing software. Email service providers often offer built-in reporting and analytics features that automatically calculate your bounce rates. These tools streamline the process and provide comprehensive insights into your campaign performance.
Monitor bounce types. Differentiating between hard and soft bounces when calculating your bounce rate will help you identify recurring issues so you can take appropriate corrective measures.
Regularly review bounce reports. Analyze bounce reports provided by your email service provider or email marketing software. By understanding the causes behind bounces, you can address them effectively.
Benchmark against industry standards. Compare your bounce rate with industry benchmarks to assess your performance. This helps you determine whether your bounce rate is acceptable or improvements are required.
What is considered an acceptable email bounce rate?
Typically, a bounce rate of less than 2% is acceptable in most email marketing campaigns.
However, it’s crucial to note that the acceptable bounce rate varies depending on the specific circumstance. For instance, a bounce rate below 1% is ideal if you have a highly engaged email list.
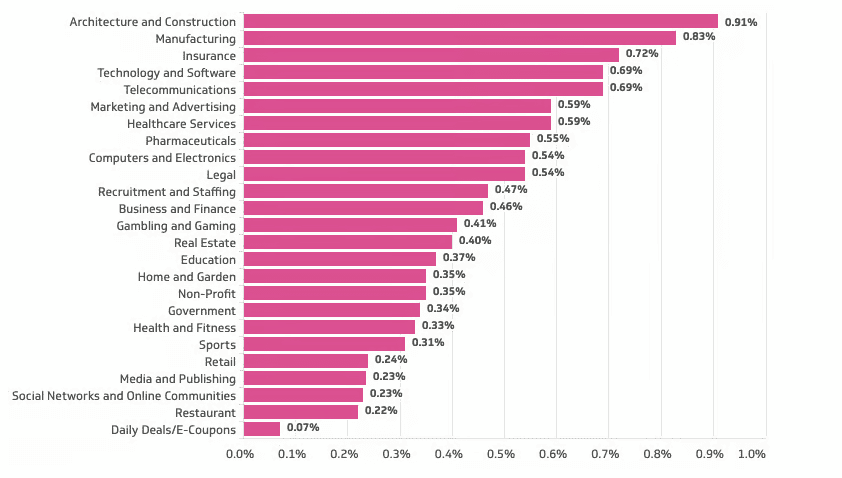
Additionally, different industries have different average bounce rates due to varying email list composure, engagement levels, and target audiences.
The image below shows different industries’ bounce back email rates.
Read also: How To Avoid Spam Filters For Better Email Deliverability
Common Reasons Why Emails Bounce
Several factors cause an email to bounce. Identifying these causes is crucial to rectifying the delivery error and maintaining a high email send score. Here are some reasons why emails bounce.
1. Invalid or non-existent email address
This happens when there is a typo in the email address or when the recipient’s email account no longer exists. An invalid email address causes a hard bounce and is the most common reason for a bounced back email.
To avoid an email bounce caused by invalid email addresses, here are a few tips to help.
- Verify subscribers’ email addresses. Implementing an email verification process is crucial to ensure the accuracy of addresses in your email list. Verification tools like BriteVerify or ZeroBounce help identify and remove invalid addresses before sending out your campaigns.
- Implement a double opt-in. This process requires users to confirm their email addresses after signing up. It reduces the chances of invalid or mistyped addresses entering your list. Additionally, it reduces email bounce rate by up to 48%.
- Clean up your list regularly. Email subscribers occasionally change their email addresses or stop engaging with your campaigns. So, it is crucial to periodically analyze engagement metrics and remove addresses that consistently bounce or show no engagement.
2. No space for new messages in the recipient’s mailbox
Trying to send an email to an address overflowing with unread messages is like stuffing a suitcase bursting at the seams.
This bounce-back error is usually resolved when the recipient’s inbox becomes freed up to receive emails. Usually, a full mailbox indicates that the user is inactive or has abandoned the email address.
Read also: Unlocking The Secrets Of Sender Reputation: Your Key To Email Deliverability
3. Service provider issues
These issues range from technical problems, like server downtime, to policy-based problems, like sending limits. Furthermore, spam filters and firewalls set up by the recipient’s email service provider can also cause an email to bounce if they perceive it as potentially harmful or unsolicited.
4. Invalid domain name
When an email is sent, the sending server performs a DNS lookup to translate the recipient’s domain name into an IP address. If the domain name doesn’t exist, the DNS lookup will fail, resulting in a DNS resolution failure.
The sending server will then receive an error response indicating that the domain does not exist. This failure typically triggers a bounce message, informing the sender that the email could not be delivered.
To minimize email bounces due to non-existent domains, ensure the accuracy and validity of recipient email addresses.
Read also: Email Sunsetting Policy 101 For Beginners
5. Email blocked by recipient’s server
Email bounces due to blocking by the recipient’s server can occur for various reasons, including strict filtering policies, suspicions of spam or malware, or the sender’s server being flagged as untrustworthy.
Resolving this issue may involve contacting the recipient to include your email sending IP address to their allowlist so that subsequent emails can be successfully delivered to them.
6. Email spam filter
According to a study, 14% of legitimate commercial emails end up in spam folders. It is worth noting that even the slightest hint of “spam-ness” in your emails can trigger a bounce; therefore, be cautious of practices that can set off spam filters, such as excessive capitalization, misleading subject lines, or suspicious attachments.
Read also: The Impact of Blacklists, Greylists, and Whitelists on Your Email Deliverability
7. Poor sender’s reputation
High spam complaint rates are the primary cause of a poor email sender reputation. When many recipients mark your email as spam, it negatively impacts your sender’s reputation. Also, using outdated or purchased email lists often results in high bounce rates and spam complaints, leading to a tarnished sender reputation.
Sending irrelevant content can also lead to a poor sender reputation. Additionally, If recipients are not interested in your email content, they are more likely to ignore them, delete them without reading them, or mark them as spam.
Read also: 29 Critical SMTP Response Codes And How To Fix Them
8. Server size limitations
Email servers often limit the size of incoming emails they can accept. These limitations are in place to manage server resources, prevent abuse, and ensure smooth email delivery. If the size of an email exceeds the recipient’s server’s specified limits, the server may bounce the email.
Email size limitations include overall message size (including attachments), maximum attachment size, or limits on the number of recipients. If your email exceeds these limits, the recipient’s server may reject it.
Read also: Avoiding The Spam Folder: An Intro To Email Deliverability
How to Identify a bounced email
Bounce back emails are easy to identify. They can be spotted in your mailbox from the subject line and email content. You can identify a bounce back email from any of the following.
The subject line
Usually, you can identify a bounced email from the subject line. For example, a subject line that says “message not sent,” “failed delivery,” or “address not found your message wasn’t delivered,” like in the image below.
Failure message
Apart from the subject line, bounced emails usually come with an error message that pinpoints the reason for the failed delivery. You’ll also find the recipient’s email address and other details in the error message, including an option to learn more about the message failure.
SMTP error code and text
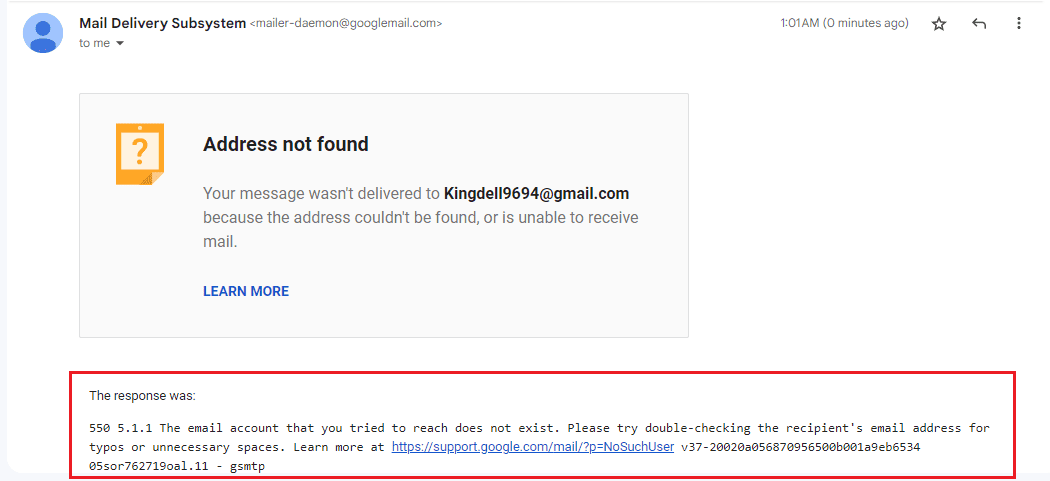
Failed email delivery report usually have an SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) code that helps you understand the reason behind the email bounce and offer solutions to prevent future emails from bouncing.
The SMTP error message usually contains a reply code, a status code, and a reply text. In the highlighted image above, 550 is the reply code, 5.1.1 is the status code, and the explanation following the status code is the reply text which describes the error code in detail.
Other frequent SMTP error codes you could find in a bounced email are as follows:
- SMTP 421 (server unavailable): This code indicates that the email server is temporarily unavailable or overloaded. It could be due to maintenance, server issues, or a high volume of incoming emails.
- SMTP 450 (mailbox temporarily unavailable): It shows temporal issues with the recipient’s mailbox, such as a full mailbox or a server undergoing maintenance.
- SMTP 541 (message rejected): This occurs due to improper formatting or attachments that exceed the recipient’s server limits and are thus rejected by the receiving server. The best way to resolve this error is by complying with the recipient’s server requirements.
- SMTP 550 (mailbox unavailable): This error occurs when the recipient’s email address is unavailable or doesn’t exist. Spam filters could also trigger it.
- SMTP 551 (mailbox doesn’t exist): This error code suggests that the recipient mailbox doesn’t exist on the receiving server.
- SMTP 554 (transactions failed): This is another SMTP error code that often arises. This is the most troublesome of all error codes because it doesn’t suggest a possible reason for the failed delivery message.
N.B. Error codes that start with 4 indicate temporal server failure from the receiving email server and will automatically attempt to resend. On the other hand, errors that start with 5 are permanent failures and usually require action to fix the problem.
Read also: ISP And Email Deliverability: How To Hit The Inbox Always
What’s Next After Receiving a Bounce Back Email?
When you receive an email bounce notification, first review the bounce notification and understand what the error message says.
As discussed earlier, bounce back messages contain error codes that help you identify the cause of the delivery failure. Understanding the specific SMTP error code or message in the bounce back email provides further insights into the reason for the bounce.
Once you have identified the reason for the bounce, it is crucial to categorize it into a type.
A hard bounce indicates that automated re-delivery is impossible. In contrast, a soft bounce suggests there may be a temporary delay in delivery, but the email will eventually be delivered, so you don’t need to worry.
If you encounter a hard bounce, removing the email address from your mailing list is advisable, as further attempts to deliver emails to that address will be futile and can harm your email send score.
To effectively handle bounce notifications, automation can be a valuable tool. Configuring a webhook to handle bounces and spam complaints can streamline the process and ensure timely action is taken.
Read also: 7 Free Email Trackers You Didn’t Know Existed
How to Reduce Your Email Bounce Rate
To improve your email bounce rate and maximize the deliverability of your campaigns, here are some best practices to follow.
- Regularly clean your email list. Remove hard-bounced email addresses promptly. Also, consider using email verification services like ZeroBounce or Bouncer to identify and remove invalid or risky addresses. EngageBay also has a free email verification tool to help you prevent hard bounces.
- Implement a double opt-in process. Major email software like EngageBay offers a double opt-in process to ensure subscribers provide a valid email address and confirm their interest in receiving your emails.
- Regularly monitor your email sender’s reputation. ISPs and email service providers often use sender reputation as a determining factor in delivering emails to the user’s inbox or spam folder. Maintain a good sender reputation by following email best practices, such as sending relevant, permission-based emails and avoiding spam triggers. This will help ensure that your emails land in subscribers’ inboxes rather than being bounced back.
- Avoid spam trigger words in your email content. Certain words and phrases like “get quick money” or “100% free” can trigger spam filters. This causes your emails to bounce or land in the spam folder. Avoiding these triggers improves email delivery rates and prevents emails from bouncing.
- Maintain a consistent sending frequency. Sending too many emails in a short period can lead to a high bounce rate. It’s essential to avoid flooding your subscribers with emails. Instead, maintain a consistent email send frequency to prevent overwhelming your subscribers and reduce the chances of email bounce.
- Use a reputable email service provider (ESP). High-quality ESPs have built-in tools to help you manage your email list and reduce bounce rates. They also have good relationships with Internet Service Providers (ISP) and email clients, which can significantly improve your email deliverability.
- Don’t exceed your daily sending limit. Each email service provider has a daily sending limit to prevent abuse. Ensure you stay within those limits to avoid bounces caused by exceeding the allowable volume.
Read also: Promotional Email – How To Write Emails That Convert
Can my ESP place limits on my account?
Yes, your Email Service Provider (ESP) can place a limit on your account. This ensures quality service for all users and prevents any email system misuse.
Limitations may include restrictions on the number of emails you can send within a specific timeframe, the size of the emails you can send, or the total storage space available. These limits are generally set to prevent spamming and to maintain server performance.
It’s important to understand that these limitations are generally outlined in the terms of the service agreement when you sign up for an email account with an ESP.
Most reputable ESPs have clear policies regarding account limits which they communicate effectively with users. If these limits are reached or exceeded, the ESP may slow down your service, block certain functionalities, or even suspend your account in extreme cases.
Hence, staying up-to-date with your ESP’s policies to avoid service disruptions is advised.
Read also: Why You Should Try Email Threads (+ Best Practices)
Top tools you’ll need to prevent an email bounce
Here are the top 3 email tools to prevent your emails from bouncing.
1. Bouncer
This email verification tool ensures the authenticity and reliability of your email lists. It works by checking each email address’s validity, thereby reducing the risk of bounced emails and protecting your sender’s reputation.
Bouncer uses advanced technology to verify syntax and domain validity. It also checks against known bounced emails and conducts a mailbox check to confirm if an email is active.
2. Emailable
Emailable verification tool enhances email marketing campaigns by ensuring the accuracy of email lists. It works by verifying the authenticity of email addresses in a list, removing duplicates, identifying spam traps, and other common issues that can negatively impact deliverability rates.
It is an intuitive tool that’s easy to use and integrates seamlessly with various email service providers.
3. NeverBounce
The core function of this tool is to eliminate invalid email addresses, reduce bounce rates, and increase deliverability.
NeverBounce uses a 20+ step proprietary cleaning process that checks each email up to 75 times from different locations around the globe. With an impressive accuracy rate, NeverBounce can distinguish between valid, invalid, catch-all, unknown, and disposable emails.
In addition to the above email verification tools, you can use email deliverability tools like Mail Tester or Spamhaus to assess the health of your email list, analyze bounce patterns, and provide insights into what might be causing the high bounce rate.
Read also: How to Write PS in Email: A Guide For Good Writing
Conclusion
Bounced emails are an inevitable part of email marketing. However, you must keep it within healthy limits to achieve your email marketing goals.
Using a reputable email service provider is crucial to reducing bounce rates and increasing email deliverability, so sign up for EngageBay’s email marketing software today.
Additionally, you can access sophisticated email marketing tools to reduce your email bounce rate and improve your deliverability when you sign up.
Book a demo with one of our experts to learn how EngageBay can help you achieve your business marketing and sales goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Bounce Back Emails
1. How should I handle a bounced email?
First, determine what type of bounce occurred. If it is a hard bounce, it means a permanent send failure occurred, and you can’t resend the message without fixing the error. In contrast, when a soft bounce occurs, it automatically makes multiple attempts to resend.
2. How do I identify the error message in my bounced email?
You can identify the error message by checking for a 3-digit code at the bottom of the failed delivery message that begins with a 4 (if the error is from the recipient’s server) or a 5 (if the error is from the sender’s server) and contains the error code and error description.
3. What is the difference between soft and hard bounces?
While both indicate delivery failure, a soft bounce represents temporary problems. In contrast, a hard bounce signifies a more permanent issue. A hard bounce is when the email is permanently rejected due to invalid addresses, or the domain does not exist. Soft bounce, on the other hand, is a temporary issue such as a full inbox or a server problem.
4. What is a fake bounce message?
A fake bounce email is a misleading error message hackers use to make a sender believe their message wasn’t delivered. These malicious actors use this method to encourage the recipient to resend the email, potentially exposing sensitive information. Therefore, it is crucial always to verify any bounce message received and ensure they originate from a legitimate source before taking further action.
5. Does a high bounce rate affect my sender’s reputation?
High bounce rates can negatively affect your sender’s reputation and reduce the deliverability of future emails. It can also lead to emails being blocked or landing in the spam folder and can skew campaign analytics giving an inaccurate picture of the campaign performance.
6. What is an acceptable bounce rate?
A bounce rate below 2% is permissible, while a bounce rate above 2% indicates a problem that needs to get fixed so as not to ruin your email send score.